A Chinese invasion of Taiwan would depend on seizing its ports. That won’t be easy.
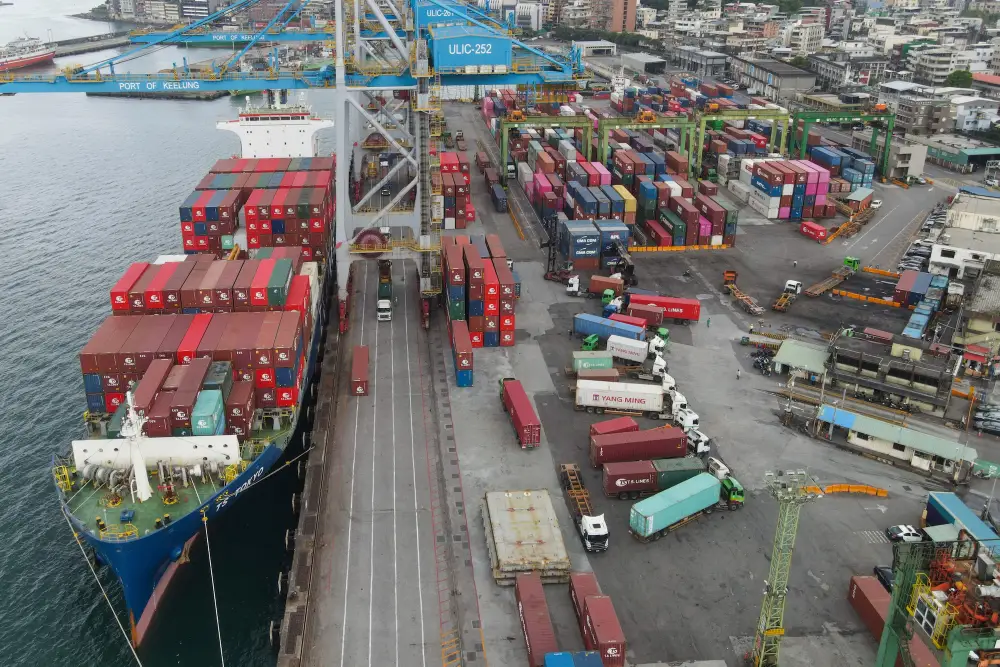

The fate of a Chinese invasion of Taiwan would turn on their effort to seize a port facility like Keelung harbor.
There are two requirements for a major amphibious invasion. The first is storming the beach.
The second is no less important — seizing a port. Without docks and cranes to unload reinforcements — especially armored vehicles — and supplies, everything has to be brought in over the open beach or flown in by helicopter. This can result in a race against time: can the invaders reinforce a large enough beachhead before the defenders try to push them into the sea?
As it contemplates an invasion of Taiwan, China is well aware of this problem. It knows full well that Taiwan will desperately defend its ports.
Chinese military journals “argue that the success or failure of an invasion of Taiwan likely would hinge on whether Chinese amphibious-landing forces are able to seize, hold, and exploit the island’s large port facilities,” naval analyst Ian Easton wrote in a new book published by the China Maritime Studies Institute at the US Naval War College.
“By themselves, Taiwan’s beaches and coastal airports are too small to land enough [People’s Liberation Army] troops, tanks, and supplies to secure a solid lodgment ashore,” Easton wrote. “Because these sites lack purpose-built infrastructure for unloading large transports and because they occupy inherently exposed positions, PLA researchers fear that Chinese landing forces could be encircled on the beaches, showered with defensive fires, and overrun by Taiwanese counterattacks.”
Chinese analysts worry that Taiwan will turn its ports into fortresses against sea assault, including mines and obstacles, sink containerships to block shipping channels, and set the waters alight by pouring oil into them.
The People’s Liberation Army, as China’s military is officially known, sees six options for taking Taiwan’s ports, all of which have disadvantages, according to Easton. A direct assault runs into the teeth of port defenses. Landing on either side of a port with armor in a pincer attack is time-consuming. Quick surprise attacks with troops in hovercraft and sea-skimming helicopters suffer from limited transport capacity. Large air assaults with helicopter-carrying troops are threatened by Taiwanese air defenses. Special operations forces may be too lightly armed to seize ports. And beach assaults like D-Day come with the risk that Taiwanese troops could bottle up the attackers.
Based on Chinese military writings, Chinese planners seem to be leaning towards a mix of these options, per Easton. An invasion would begin with heavy air, missile and naval bombardment, followed by commandos to knock out coastal defenses. “After beach obstacles and coastal fortifications have been destroyed using direct fires, large amphibious forces will make landings from the sea, supported by troops arriving by helicopters, hovercraft, and ultralights,” Easton wrote. “Once ashore, amphibious-assault units will conduct pincer movements from the beaches, surrounding port zones and isolating defenders into pockets of resistance.”
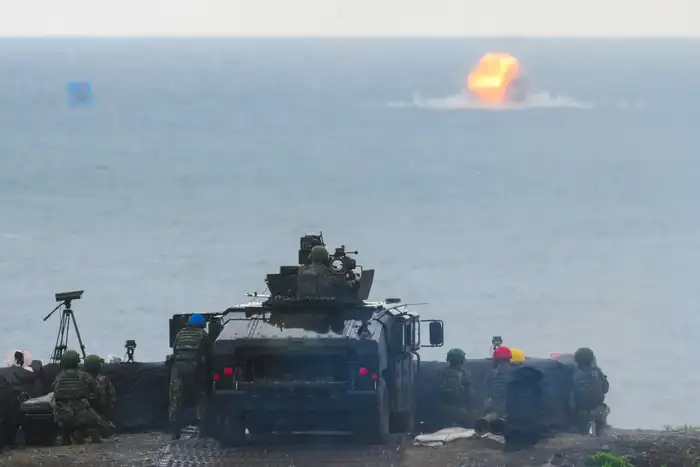

Taiwanese forces train to defend against threats at sea, and in this exercise fired a US-made anti-tank missile.
Once ashore, PLA troops will attack areas near the port from two sides at the same time as other assault units in low-flying helicopters and hovercraft strike at the port directly. Once it is captured, Chinese forces will dig in to resist a counterattack, while engineers repair the docks and clear the shipping lanes.
The ports most likely to be attacked are those “that could support the rapid off-loading of main battle tanks and other heavy equipment. The ideal candidates for attack would be well-developed commercial or industrial ports flanked by beaches and river deltas in relatively flat and lightly urbanized areas,” wrote Easton. The port of Taichung on the west coast of Taiwan is the most probable candidate, followed by Kaohsiung, Mailiao, Anping and Taiwan’s capital Taipei.
Would this Chinese strategy work? Historically, armies and navies have avoided attacking heavily defended ports directly (“A ship’s a fool to fight a fort,” said the legendary British admiral Horatio Nelson). The most infamous example is the disastrous raid on the port of Dieppe in northern France by 10,000 Allied troops (the majority of them Canadian) in August 1942. Intended as a test operation for D-Day, the attackers suffered 5,000 dead and wounded, or about the half of the assault force. The lesson was so stinging that the Allies opted to make the Normandy invasion over the beaches, and then go on to capture a port.
The challenge isn’t just seizing a port, but also getting it in usable enough condition to allow tanks to be unloaded. As the Allies discovered while taking fortified ports such as Brest and Cherbourg in 1944, the Germans made such effective use of demolitions that the port facilities were inoperative for months.
Easton suggests that Taiwan can beef up its port defenses, including missiles and mines, as well as units specially trained in urban warfare. Easton also believes that a first step could be removing the Chinese presence from Taiwanese ports, despite China accounting for 40% of Taiwan’s exports. “Taiwanese leaders could close [Chinese Communist Party]-controlled representative offices,” Easton wrote. “They could remove and replace critical port infrastructure that is linked to the Chinese military.”
In the end, the fate of an invasion of Taiwan turns on which side controls the ports. “The imagination-crushing dimensions of a PLA amphibious operation against Taiwan — the moving of millions of humans and machines — all rely on robust logistics lines,” Easton wrote. “Without them, everything else quickly crumbles and falls apart.”