Innovations in glass technology are driving progress in energy, sustainability, and consumer products. Here’s what that looks like.
SCHOTT’s advanced glass materials support an AI-driven future.
By Bill James, head of research and development at SCHOTT North America
In laboratories and factories across the globe, developers are creating cutting-edge technologies that could reshape how we live. Behind many of these breakthroughs lies an unexpected hero: a material that has been with us for centuries and is powering the next era of high-tech industries.
Since Otto Schott invented specialty glass in 1884, the simple material has become a cornerstone of modern technology, and driving innovation. Its unique properties make it indispensable across a wide range of industries that shape our daily lives. From semiconductors to clean energy, home tech, and electric vehicles, glass is the silent enabler of progress.
Powering next-generation semiconductors
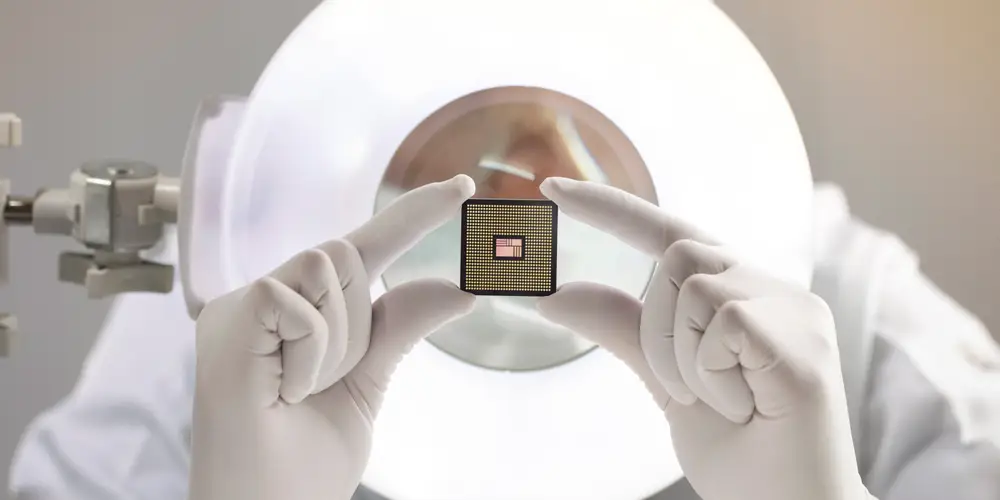
With AI on the rise, industries need more powerful microchips with increased performance to handle large amounts of data, which must be processed at high speed while consuming energy efficiently.
Glass carriers and substrates are promising materials at the heart of this revolution, enabling remarkable performance gains in chip packaging. Industry analysts predict high-end performance packaging will reach $28.4 billion by 2029, fueled by the growing adoption of AI, 5G and 6G networks, and other data-intensive technologies that will require powerful, efficient chips.
Chips packaged with glass substrates can achieve up to 40% better performance while using only half the power of their plastic-packaged counterparts.
Glass’ versatility — such as customizable thermal expansion, high stiffness, ultra-smooth surfaces, electrical properties, and optical transparency — meets the demanding needs of advanced manufacturing and packaging solutions.
Bringing smart glasses and AR to the masses
Augmented reality (AR) is set to transform industries by merging digital and physical worlds, creating interactive experiences in entertainment and gaming, and enhancing remote collaboration with interactive 3D models. As this technology evolves, its applications will broaden, fostering innovation and efficiency across various sectors, particularly when combined with emerging technologies like 5G, AI, and IoT.
As the US leads in software and hardware innovation, the photonics industry is poised to become a key enabler of AR optics. Glass, in the form of optical waveguides, channels digital information to the eye when wearing smart glasses. Thanks to its advanced properties and characteristics, glass processing is projected to scale and lower costs in the coming years, paving the way for mass-market smart glasses.

SCHOTT’s waveguide solutions are designed to meet the growing worldwide demand for smart glasses.
Unlocking fusion energy
The quest for fusion energy — the holy grail of clean, limitless power — has taken a giant leap forward, and glass is at the heart of this breakthrough. Specially engineered laser glass helped researchers achieve what was once thought impossible: creating more energy from a reaction than was put into it.
In a groundbreaking experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, scientists used 192 powerful laser beams to replicate conditions like those at the center of the sun. The light, amplified by active laser glass and focused through precisely crafted optical glass, delivered significant energy to a tiny fuel pellet, triggering a fusion reaction that produced a net energy gain.
The fusion reaction generated 3.15 megajoules of energy, exceeding the 2.05 megajoules of laser energy delivered to the target. This net energy gain, albeit small, demonstrates that with the right technology — including advanced glass — we can replicate the sun’s power on Earth. Subsequent experiments have produced even larger yields. As scientists refine fusion energy, glass will be vital in scaling up reactors, helping to focus laser light and withstanding extreme conditions, positioning it at the core of this transformative technology that could revolutionize global energy.
Advancing electric vehicles
Today’s electric cars mostly rely on lithium-ion batteries, a technology that was introduced commercially in the 1990s. In the future, solid-state battery technology aims to advance electric vehicles even further.
At the heart of this innovation is a surprising material: glass-ceramic powder. It boasts high conductivity, exceptional chemical and temperature stability, and improved performance. Most importantly, it enables the use of lithium metal anodes, which have ten times the storage capacity of current graphite anodes. This translates to electric vehicles that can travel up to 30% further on a single charge.
Using this technology, charging an EV to 80% in just 10 minutes is on the horizon. The road to commercialization is still long, with mass production of solid-state battery-equipped vehicles forecasted to start around 2030. Glass-ceramic will play an outsized role as adoption continues to grow.
Modernizing everyday kitchens
Specialty glass is also redefining smart kitchens, allowing advanced technology to blend into sleek, modern designs. Recent breakthroughs in glass ceramics like SCHOTT CERAN Luminoir® TFT have allowed cooktops to display vibrant, high-resolution visuals, beyond traditional white and blue light. These materials can integrate smart displays that remain hidden when not in use, providing a clean, elegant appearance that makes cooktops smarter and more interactive without compromising design for an intelligent user experience.
The true value lies in how these surfaces enhance cooking experiences by featuring fully functional screens with perfect resolution. Information such as cooking temperatures, timers, and step-by-step recipe instructions is clearly displayed on the surface. The glass efficiently transmits light, even at low brightness, ensuring optimal visibility without excess energy consumption. This innovation promises to revolutionize kitchen design by merging cutting-edge technology with the joy of cooking.
The story of glass in high-tech industries is a testament to human ingenuity and the power of materials science. As we continue to face global energy, sustainability, and healthcare challenges, the innovations emerging from glass-research labs worldwide offer hope and exciting possibilities. The future is as clear as a well-polished window pane — glass will play a crucial role in building a more efficient, sustainable, and innovative world.