Stocks might ‘go nowhere’ for the rest of this year amid Fed uncertainty and US debt concerns, market vet says

The stock market could be bumping up against a ceiling for now, market veteran Ed Yardeni said.
The longtime investor and president of Yardeni Research said he sees limited capacity for central bankers to cut interest rates, thanks to the strength of the US economy and a troubling outlook for the federal debt balance.
That means further policy easing may not come until 2025 — and the S&P 500 could stay stuck around 5,800 through the end of the year, he said in a recent note to clients.
That would imply less than a 1% gain for the benchmark index in the next two months.
Stocks have already been going “nowhere fast” since the Fed issued a jumbo-sized rate cut in September, Yardeni said. The S&P 500 has climbed 2% since the Fed’s last policy meeting, while the S&P 500 equal-weighted index has risen 3.8%.
“We expect that it might go nowhere fast over the rest of this year too, hovering around 5,800. The outlook for fiscal policy will probably remain unsettling after the election and the Fed might not lower the FFR over the rest of this year after all,” Yardeni wrote.
Yardeni pointed to strength in recent economic data, which suggests that further rate cuts might not come out of the Fed’s meeting this week or in December.
For one, real GDP growth was strong in the third quarter, rising 2.8% year-over-year.
Business equipment investment rose 11% over the third quarter, following a near-10% increase in the prior quarter. Investment in information processing equipment, in particular, hit a record high, according to data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
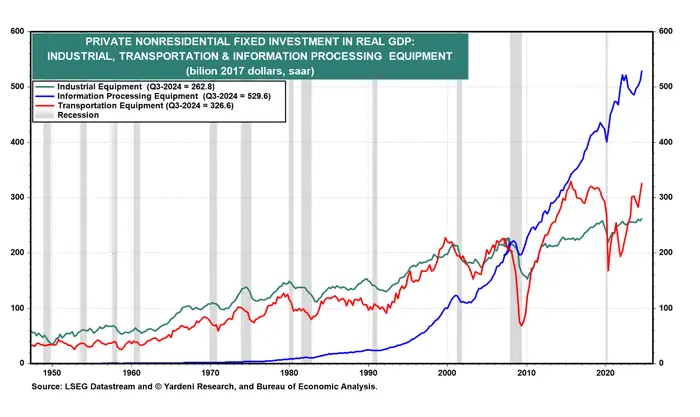
Business equipment investment continued to rise over the third-quarter.
Weakness in the job market has concerned some investors, with the US adding far fewer payrolls than expected in October. Yet, analysts have said the labor market weakness was at least partly the result of events including union strikes and Hurricanes Helene and Milton.
Importantly, the unemployment rate remained near a historic low last month at 4.1%.
“The bond market agrees with our opinion that the Fed cut the FFR too much, too soon,” Yardeni added, pointing to the recent rise in bond yields, which indicate higher interest rate expectations among bond investors.
Government borrowing, meanwhile, looks poised to increase over the coming months, a factor economists have said could indirectly fuel inflation, and therefore limit the Fed’s ability to cut rates.
“What can we expect when the current debt limit suspension ends on January 2? A divided government could force the Treasury to use extraordinary measures (as it did early last year) to fund the government while Congress debates the ever-increasing debt limit. It may take a debt crisis in the bond market to rein in Washington’s fiscal excesses,” Yardeni said.
Yardeni has warned clients before about the possibility that no further rate cuts are delivered by the Fed in 2024. However, most investors expect the Fed to cut rates by 25 basis points this week and cut by the same amount in December, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
Some forecasters have even floated another jumbo-sized rate cut this year as the labor market could be weaker than it appears on the surface.